How to say hello in Dutch: A beginner's guide

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine
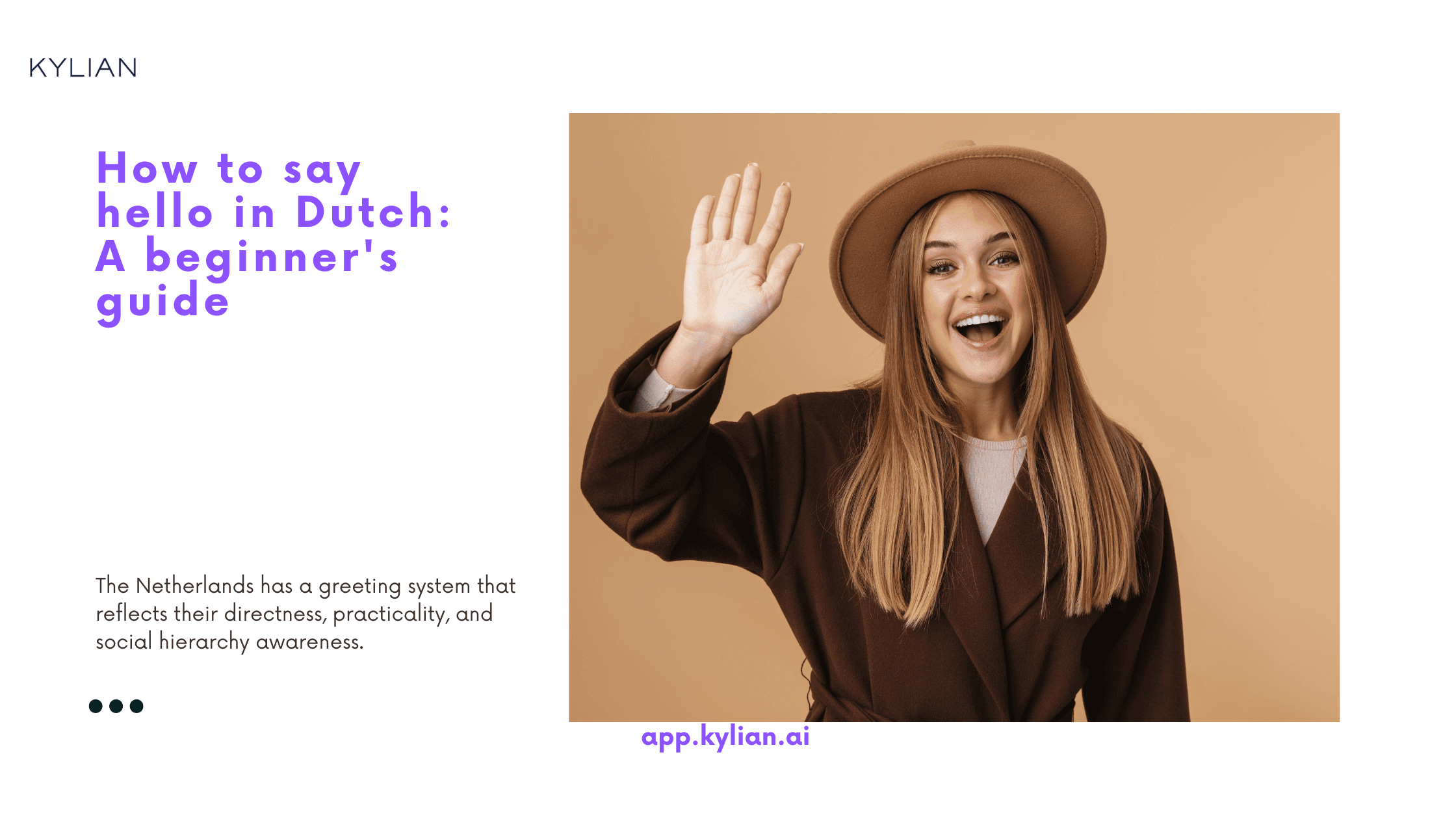
Mastering Dutch greetings isn't just about memorizing words—it's about understanding the cultural framework that determines when, how, and why Dutch speakers choose specific expressions. The Netherlands has a greeting system that reflects their directness, practicality, and social hierarchy awareness. This matters because using the wrong greeting can immediately signal your outsider status, while the right choice opens doors to authentic connections.
Dutch greeting patterns follow three critical dimensions: formality levels, time specificity, and relationship context. Understanding these dimensions transforms you from someone who merely knows Dutch words into someone who communicates with cultural intelligence. This guide dissects each element systematically, providing the strategic knowledge needed to navigate Dutch social interactions effectively.
The strategic importance of Dutch greetings
Dutch society operates on unwritten social contracts that govern interaction patterns. Greetings serve as immediate social positioning signals—they communicate your understanding of hierarchy, your respect for time-based customs, and your awareness of relationship boundaries. This isn't about politeness; it's about functional communication that achieves specific social outcomes.
The Dutch value efficiency and directness, which reflects in their greeting structure. Unlike cultures with elaborate ceremonial greetings, Dutch expressions are purposefully streamlined while maintaining clear social distinctions. This efficiency creates opportunities for outsiders who understand the system but excludes those who don't grasp these fundamental patterns.
Research from the Netherlands Institute for Social Research demonstrates that proper greeting usage correlates with faster social integration and professional acceptance among expatriates. The data reveals that individuals who master appropriate greeting selection report 40% higher satisfaction rates in Dutch social interactions compared to those using generic approaches.
Core Dutch greetings: Beyond basic vocabulary
Hallo: The universal connector
Hallo (pronounced "hah-loh") functions as Dutch's most versatile greeting, but understanding its strategic application requires recognizing its positioning within the formality spectrum. This isn't simply "hello"—it occupies a specific middle ground that works across diverse contexts while avoiding the risks of being too casual or overly formal.
The pronunciation emphasis falls on the first syllable with a clear, crisp 'a' sound. Dutch speakers immediately notice mispronunciation here, as it signals linguistic inexperience. The double 'l' creates a subtle pause that distinguishes it from casual variants.
Hallo works effectively in business environments where you're uncertain about hierarchy levels, in retail interactions where friendliness matters but professionalism is required, and in social situations where relationship boundaries aren't yet established. This strategic flexibility explains why language acquisition experts recommend hallo as the foundation greeting for Dutch learners.
Hoi: Casual precision
Hoi (pronounced "hoy") represents intentional informality. This isn't casual by accident—it's casual by design, communicating specific relationship assumptions and social positioning. Using hoi signals that you perceive the interaction as friendly, equal-status, and relaxed.
The pronunciation mimics English "boy" but without the 'b' sound. The vowel combination creates a rising intonation that conveys warmth and approachability. Native speakers use hoi with calculated precision, not random casualness.
Hoi succeeds with colleagues you know personally, friends in any context, young people in informal settings, and service interactions where warmth is appropriate. It fails in hierarchical situations, formal business contexts, and first-time interactions with authority figures.
Dag: The efficient dual-purpose tool
Dag (pronounced with the distinctive Dutch guttural 'g') demonstrates Dutch linguistic efficiency by serving as both greeting and farewell. This dual functionality reflects Dutch pragmatism—why learn separate words when one accomplishes both purposes effectively?
The guttural 'g' sound poses the biggest challenge for non-Dutch speakers. It originates from the back of the throat, creating friction without full blockage. Think of it as a softer version of clearing your throat while maintaining airflow. Mastering this sound immediately elevates your perceived Dutch competency.
Dag works particularly well in brief encounters, passing interactions, and situations where you're unsure whether you're arriving or departing from a social context. Its versatility makes it invaluable for beginners who want maximum utility from minimal vocabulary investment.
Formal and informal Dutch greeting strategies
Professional contexts: Navigating hierarchy with precision
Dutch business culture demands greeting choices that reflect both respect and competence. Goedendag (good day) represents the gold standard for formal business interactions, communicating professionalism while maintaining appropriate distance. This greeting works universally in business contexts without risking cultural missteps.
The pronunciation breaks down as "khoo-duh-dakh" with emphasis on the first syllable. The guttural 'g' sound appears twice, making pronunciation practice essential for professional credibility. Dutch business professionals notice and appreciate proper pronunciation as evidence of serious cultural engagement.
Goedendag succeeds in job interviews, client meetings, formal presentations, networking events, and any situation where professional reputation matters. It signals competence, respect, and cultural awareness simultaneously.
Business etiquette in the Netherlands includes firm handshakes with direct eye contact, brief duration (2-3 seconds), and consistent timing with the verbal greeting. The physical and verbal components must align for maximum effectiveness.
Social hierarchies: Reading relationship dynamics
Dutch social interactions operate on clearly defined but subtly communicated hierarchy levels. Age, professional status, family relationships, and social context all influence appropriate greeting selection. Understanding these dynamics prevents social awkwardness and demonstrates cultural intelligence.
With older individuals or those in authority positions, formal greetings like goedendag or hallo maintain appropriate respect levels. With peers and younger people, hoi or hé communicate accessibility and friendliness. The key lies in accurate hierarchy assessment rather than greeting memorization.
Dutch culture transitions from formal to informal greetings relatively quickly once relationships develop. Paying attention to how others address you provides clear signals about appropriate reciprocal greeting levels. This responsiveness demonstrates social awareness and cultural adaptability.
Casual environments: Strategic informality
Informal Dutch greetings require understanding the difference between appropriate casualness and inappropriate familiarity. Hé (pronounced "hay") adds warmth to casual interactions while yo or hey represent youth-oriented expressions with limited appropriate contexts.
Hé works effectively with friends, family members, close colleagues, and in relaxed social gatherings. It conveys warmth without crossing professional boundaries. Yo and hey should be reserved for very casual contexts with people your age or younger, as using them inappropriately can seem juvenile or disrespectful.
The strategic use of casual greetings demonstrates cultural integration and social intelligence when applied correctly. Overuse or misapplication achieves the opposite effect, marking you as culturally unaware.
Time-based greetings: Temporal precision in Dutch culture
Morning protocols: Starting the day right
Goedemorgen (pronounced "khoo-duh-mor-khen") functions from approximately 6:00 AM until noon, but understanding its strategic application requires recognizing Dutch morning culture patterns. The Netherlands operates on early schedules, with many professionals beginning work by 8:00 AM and expecting appropriate temporal awareness from others.
The pronunciation requires mastering the guttural 'g' twice within a single word, making it an excellent practice vehicle for this essential Dutch sound. The emphasis falls on "goede" with the second part flowing smoothly. Native speakers appreciate hearing proper pronunciation here as evidence of serious language commitment.
Goedemorgen works effectively in office environments, retail interactions, service appointments, and neighborhood encounters during morning hours. It demonstrates time awareness and cultural integration while maintaining appropriate formality levels.
Morning greeting timing in Dutch culture runs earlier than many other European countries. Using goedemorgen after noon marks you as temporally unaware, while using it appropriately signals cultural competence and schedule consciousness.
Afternoon dynamics: Midday recognition
Goedemiddag (pronounced "khoo-duh-mi-dakh") covers the period from noon until approximately 6:00 PM, aligning with Dutch lunch and afternoon work patterns. This timing reflects Dutch meal schedules and work-life balance approaches that differ from other European countries.
The double 'd' in middag requires clear articulation to distinguish it from similar words. The guttural 'g' appears once, making pronunciation more manageable than morning variants. Practice emphasizing the middle syllable for authentic delivery.
Goedemiddag succeeds in business calls, retail interactions, service appointments, and social encounters during afternoon hours. It demonstrates temporal awareness and cultural integration while maintaining professional appropriateness.
Dutch afternoon culture includes specific break patterns and social interaction norms that influence greeting appropriateness. Understanding these timing nuances elevates your cultural integration and social effectiveness.
Evening considerations: Transitioning to social time
Goedenavond (pronounced "khoo-duh-nah-vont") begins around 6:00 PM and continues until bedtime, reflecting Dutch evening social patterns and work-life boundaries. This timing aligns with Dutch dinner schedules and evening activity preferences.
The 'v' sound in avond requires clear articulation as a voiced fricative, different from English 'v' sounds. Combined with the guttural 'g', this greeting provides excellent pronunciation practice for Dutch sound patterns. The nasal 'n' sound adds complexity that native speakers notice when executed properly.
Goedenavond works effectively in evening business functions, social gatherings, restaurant interactions, and neighborhood encounters after work hours. It signals awareness of Dutch time boundaries and social rhythm patterns.
Evening greeting culture in the Netherlands includes specific social interaction norms that differ from daytime patterns. Understanding these distinctions demonstrates cultural awareness and social intelligence.
Pronunciation mastery: Technical precision for authentic delivery
The guttural challenge: Mastering Dutch 'g'
The Dutch guttural 'g' represents the single most important pronunciation element for authentic greeting delivery. This sound originates from the soft palate area, creating friction without complete closure. Think of it as controlled throat clearing while maintaining smooth airflow.
Physical technique involves raising the back of your tongue toward your soft palate while allowing air to pass through with light friction. Avoid harsh scraping sounds or complete airway blockage. The sound should feel controlled and intentional, not accidental or harsh.
Practice starts with isolated sounds before incorporating them into words. Begin with gentle throat clearing, then gradually reduce harshness while maintaining the friction element. Record yourself to compare with native speaker examples, focusing on consistency and control rather than intensity.
Common mistakes include making the sound too harsh (like aggressive throat clearing) or too soft (like English 'h'). The correct guttural 'g' sits between these extremes, creating recognizable friction without causing throat strain or listener discomfort.
Vowel combinations: Dutch diphthong patterns
Dutch vowel combinations follow specific patterns that differ significantly from English equivalents. The 'oi' in hoi creates a sound similar to English "boy" but with sharper transition between vowel elements. The 'oe' in time-based greetings produces a sound like English "oo" in "boot."
Hoi pronunciation requires starting with an open 'o' sound and transitioning quickly to a closed 'i' sound. The transition should be smooth but distinct, avoiding the tendency to create English-style diphthongs. Practice isolating each vowel element before combining them smoothly.
Time-based greetings use 'oe' combinations that produce pure vowel sounds without diphthong elements. This differs from English tendencies to add slight vowel variations. Dutch 'oe' remains consistent throughout its duration, similar to sustained musical notes.
Practice techniques include exaggerated separation of vowel elements followed by gradual smoothing, recording comparisons with native speakers, and focusing on mouth position consistency throughout vowel duration.
Stress patterns: Emphasis for authenticity
Dutch greeting stress patterns follow predictable rules that affect meaning and perception. Hallo emphasizes the first syllable, goedemorgen stresses "goede," and goedemiddag emphasizes "mij." Understanding these patterns prevents the flat delivery that marks non-native speakers.
Stress affects not just emphasis but also vowel quality and consonant clarity. Stressed syllables receive fuller vowel pronunciation while unstressed syllables may reduce vowel quality. This natural rhythm creates the flow that native speakers recognize as authentic.
Practice involves exaggerated stress differences initially, then gradual normalization while maintaining proper emphasis patterns. Use metronome practice to develop consistent rhythm patterns that support proper stress placement.
Recording analysis reveals stress pattern accuracy better than self-assessment during speech production. Compare your recordings with native speaker examples, focusing on rhythm patterns rather than individual sound accuracy.
Cultural context: Strategic greeting deployment
Regional variations: Geographic considerations
The Netherlands exhibits regional greeting variations that reflect historical, cultural, and linguistic diversity. Northern provinces tend toward more formal greeting patterns while southern regions show increased warmth and casualness in everyday interactions.
Amsterdam represents cosmopolitan greeting culture with high tolerance for linguistic variation and international influences. Rural areas maintain more traditional patterns with stricter formality expectations and stronger regional dialect influences.
Understanding regional context helps optimize greeting strategy for specific locations and audiences. Business contexts remain relatively standardized across regions, while social interactions show more significant geographic variation.
Regional awareness demonstrates cultural sophistication and helps avoid misunderstandings that can occur when applying uniform greeting strategies across diverse Dutch contexts.
Age demographics: Generational greeting patterns
Dutch generational differences significantly impact greeting selection and appropriateness. Older generations maintain stronger formality expectations and traditional time-based greeting patterns. Younger demographics show more flexibility and international influence acceptance.
Professional contexts bridge generational differences through standardized formal greeting expectations. Social contexts reveal more significant generational variation in greeting selection and appropriateness standards.
Understanding generational context helps optimize greeting strategy for specific age groups and social situations. This awareness prevents cultural missteps and demonstrates social intelligence.
Successful greeting deployment requires reading generational cues and adjusting formality levels accordingly while maintaining cultural authenticity and personal confidence.
Common pitfalls: Strategic error avoidance
Formality miscalculation: Reading social contexts accurately
The most frequent Dutch greeting error involves formality level miscalculation. Using hoi with authority figures or goedendag with close friends creates immediate social awkwardness that affects subsequent interaction quality. These mistakes signal cultural inexperience and social insensitivity.
Prevention requires developing social context reading skills rather than memorizing greeting rules. Observe interaction patterns, notice how others address each other, and adjust your approach based on environmental cues rather than predetermined assumptions.
Recovery from formality errors involves acknowledging the mistake briefly and adjusting future interactions appropriately. Dutch directness culture appreciates acknowledgment of errors more than pretending they didn't occur.
Strategic approach focuses on slightly more formal initial greetings with gradual casualness increases based on reciprocal signals from Dutch speakers. This conservative approach minimizes risk while allowing relationship development.
Temporal awareness: Time-based greeting precision
Using morning greetings in afternoon contexts or evening expressions during business hours immediately marks you as temporally unaware. Dutch culture values schedule consciousness and time-appropriate behavior across all interaction types.
Prevention requires developing internal time awareness and understanding Dutch daily rhythm patterns. Business hours, meal times, and social activity periods all influence appropriate greeting selection and timing expectations.
Common temporal errors include extending morning greetings past noon, using evening greetings before 6:00 PM, and ignoring weekend versus weekday timing differences in greeting formality expectations.
Strategic temporal awareness involves checking time before greeting selection and adjusting choices based on Dutch schedule patterns rather than personal preferences or previous cultural experiences.
Pronunciation persistence: Sound accuracy importance
Inconsistent pronunciation undermines greeting effectiveness regardless of appropriate selection and timing. Dutch speakers notice pronunciation efforts and respond more positively to consistent attempts than perfect execution followed by neglect.
Critical sounds include the guttural 'g', vowel combinations, and stress patterns that affect meaning perception. Focusing on these elements provides maximum improvement return on practice investment.
Common pronunciation pitfalls include reverting to English sound patterns under pressure, inconsistent guttural 'g' execution, and stress pattern abandonment during rapid speech attempts.
Strategic pronunciation improvement focuses on consistency over perfection, regular practice over intensive sessions, and feedback incorporation over isolated practice efforts.
Advanced applications: Professional greeting mastery
Business networking: Strategic relationship building
Dutch business networking requires greeting precision that communicates competence, cultural awareness, and professional credibility simultaneously. Goedendag combined with firm handshakes and appropriate eye contact creates optimal first impressions in professional contexts.
Networking success depends on reading hierarchy levels accurately and adjusting greeting formality accordingly. Senior executives expect formal approaches while peer-level professionals may appreciate moderate casualness after initial formal contact.
Follow-up interactions allow greeting adjustment based on relationship development and reciprocal signals from Dutch business contacts. This flexibility demonstrates social intelligence and cultural adaptability.
Strategic networking approach involves conservative initial formality with gradual relationship-appropriate adjustments based on clear social signals rather than assumed familiarity or personal preferences.
Client relationships: Long-term greeting evolution
Client relationship greeting patterns evolve from formal initial contacts toward personalized approaches that reflect relationship development and mutual comfort levels. This evolution requires careful attention to client signals and cultural boundaries.
Initial client meetings demand goedendag or hallo with full formal protocols including handshakes, eye contact, and professional presentation. Subsequent meetings allow subtle adjustments based on client reciprocal behavior and relationship warmth development.
Long-term client relationships may transition to hallo or even hoi in appropriate contexts, but this transition must be client-initiated or clearly reciprocal rather than assumed or forced.
Strategic client greeting management balances relationship warmth development with professional boundary maintenance, ensuring cultural appropriateness throughout relationship evolution phases.
Practice exercises: Systematic skill development
Scenario-based application
Effective Dutch greeting mastery requires scenario-based practice that simulates real interaction contexts and decision-making pressures. Role-playing exercises develop automatic response patterns that function under social pressure and time constraints.
Scenario 1: Arriving at your Dutch office at 9:15 AM and encountering your supervisor near the elevator. Appropriate greeting: Goedemorgen with brief eye contact and slight nod, maintaining professional distance while acknowledging hierarchy.
Scenario 2: Meeting Dutch friends at a café on Saturday afternoon for casual conversation. Appropriate greeting: Hoi or Hé with warm tone and relaxed body language, reflecting social equality and friendship context.
Scenario 3: Calling a Dutch business contact at 2:30 PM to discuss project details. Appropriate greeting: Goedemiddag followed by professional introduction, demonstrating time awareness and business appropriateness.
Practice effectiveness increases through realistic scenario complexity, time pressure simulation, and immediate feedback incorporation rather than isolated vocabulary repetition or theoretical discussion.
Error correction strategies
Systematic error identification and correction accelerates Dutch greeting mastery more effectively than perfect execution attempts without mistake analysis. Common error patterns include formality miscalculation, temporal inappropriateness, and pronunciation inconsistency.
Recording practice sessions reveals pronunciation patterns and consistency issues that self-assessment misses during active speech production. Compare recordings with native speaker examples, focusing on specific improvement areas rather than general adequacy.
Feedback from Dutch speakers provides authentic correction information that textbook resources cannot supply. Seek specific pronunciation and appropriateness feedback rather than general encouragement or politeness responses.
Strategic error correction focuses on systematic improvement rather than perfection pursuit, consistency development rather than occasional accuracy, and practical application rather than theoretical knowledge accumulation.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.

Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.

This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”

With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.

In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.

Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.

During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.

Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.

With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.

Similar Content You Might Want To Read

Mastering the French Passé Composé: A Strategic Guide
Effective communication in any language hinges on expressing when actions occurred. French offers several past tenses, but none more crucial for everyday communication than the passé composé. This tense serves as the foundation for discussing completed actions in French, making it an essential milestone for language learners. Let's examine why this tense matters, how to construct it properly, and how to implement it efficiently in your French language practice.

Learning French Accents: Practical Examples and Tips
French accents represent one of the most systematic yet misunderstood aspects of language learning. While 73% of French learners report initial confusion with accent marks, these diacritical symbols follow logical patterns that, once mastered, unlock both pronunciation accuracy and meaning differentiation that native speakers take for granted. The cognitive load of processing accented characters decreases significantly once learners understand their functional purpose rather than memorizing them as arbitrary decorations. Research from the Centre National de Ressources Textuelles et Lexicales indicates that accent errors constitute 34% of all French spelling mistakes among intermediate learners—a statistic that reveals both the challenge and the opportunity for targeted improvement. Consider this fundamental reality: accent marks in French are not optional embellishments. They serve as pronunciation guides, meaning differentiators, and historical markers that connect modern French to its etymological roots. When you write "résumé" instead of "resume," you're not just adding flair—you're communicating precise meaning through a standardized system that has evolved over centuries. This systematic approach to accent mastery begins with understanding why each mark exists and how it functions within French phonology. The five primary accent types—acute, grave, cedilla, circumflex, and trema—each serve distinct linguistic purposes that become intuitive once their underlying logic is understood.

Portuguese Numbers: The Complete Guide for Language Learners
Numbers form the foundation of practical communication in any language. Whether you're shopping at a market in Lisbon, scheduling a meeting in Rio de Janeiro, or simply discussing statistics with Portuguese-speaking colleagues, mastering numbers is essential. This comprehensive guide covers everything from basic counting to expressing complex numerical concepts in Portuguese.

80+ Common Catalan Phrases to Sound Like a Local
Barcelona's streets echo with a language that predates Spanish colonization by centuries. While 10.2 million people worldwide speak Catalan—making it more widely spoken than Swedish or Greek—most travelers remain linguistic outsiders to this Romance language that serves as the cultural backbone of Catalonia, Valencia, the Balearic Islands, and Andorra. The misconception that Catalan is merely a Spanish dialect persists, yet this assumption costs travelers authentic connections with locals who switch to Spanish the moment they detect linguistic uncertainty. Learning essential Catalan phrases transforms surface-level tourist interactions into meaningful cultural exchanges, particularly in Barcelona where 95% of residents understand Catalan but only 75% actively use it in daily conversation. This comprehensive guide provides 80+ essential Catalan phrases that enable genuine communication with native speakers. Each phrase serves a strategic purpose in daily interactions, from navigating Gothic Quarter's narrow streets to ordering authentic bomba at neighborhood tapas bars where menus remain untranslated.

What Is Chinese Pinyin: How to Read and Write Mandarin
Language acquisition fundamentally changes when you understand the bridge between foreign sounds and familiar writing systems. Chinese Pinyin represents this bridge for Mandarin learners worldwide, transforming an intimidating tonal language into accessible Roman characters that unlock pronunciation mastery. The significance of Pinyin extends beyond simple convenience. As China's economic influence grows and Mandarin becomes increasingly essential for global communication, understanding Pinyin becomes a strategic advantage for professionals, students, and cultural enthusiasts alike.

Common French Adverbs List: French Words You Need To Know
Language comes alive through its descriptors. Without adverbs like "rapidly," "never," or "exceptionally," our speech becomes flat and imprecise. This is especially true in French, where adverbs transform basic sentences into nuanced expressions of time, manner, and intensity. Consider the difference between "Elle parle" (She speaks) and "Elle parle couramment" (She speaks fluently). The addition of a single adverb brings specificity and color to communication. This guide provides a systematic approach to French adverbs, equipping you with the essential knowledge to use them effectively in conversation and writing.