Learning About The Baybayin Alphabet: Complete Guide

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine
The resurgence of indigenous writing systems represents more than cultural nostalgia—it signals a fundamental shift in how societies reclaim their intellectual heritage. Baybayin, the pre-colonial script of the Philippines, exemplifies this phenomenon. While most ancient writing systems remain archaeological curiosities, Baybayin thrives in contemporary contexts, from government legislation to social media hashtags.
This revival matters because language shapes thought, and writing systems preserve the cognitive frameworks of entire civilizations. When communities abandon their indigenous scripts, they lose more than symbols—they surrender unique ways of conceptualizing communication itself.
Understanding the Historical Context of Baybayin
The term "Baybayin" derives from the Tagalog root "baybay," meaning "to spell" or "to write." This etymology reveals something crucial: the script wasn't imposed by external forces but emerged organically from Filipino linguistic structures. The widespread misuse of "alibata"—a 20th-century fabrication without historical foundation—demonstrates how colonial disruption can distort even basic terminology.
Archaeological evidence positions Baybayin within the broader Brahmic script family, connecting it to writing systems across Southeast Asia including Javanese, Balinese, and Bugis scripts. This genealogy traces back to the ancient Brahmi script of India, establishing Baybayin as part of a sophisticated intellectual network that spanned maritime Asia long before European contact.
The Laguna Copperplate Inscription, dating to 900 CE, provides the earliest known example of Brahmic script usage in the Philippines. While not strictly Baybayin, it demonstrates that literate traditions in the archipelago predate Spanish colonization by over six centuries. The Monreal stone offers additional evidence of indigenous writing practices, challenging colonial narratives that portrayed pre-contact Philippines as illiterate.
Spanish chroniclers consistently noted the prevalence of literacy among Filipinos. Friar Pedro Chirino's 1604 observation that virtually everyone in Manila could read and write using Baybayin contradicts colonial assumptions about indigenous intellectual capacity. This widespread literacy suggests a society that valued written communication and maintained educational systems capable of producing literate populations.
The Spanish response to Baybayin reveals colonial pragmatism. Rather than immediately suppressing the script, missionaries like Francisco López incorporated it into religious texts. The 1593 "Doctrina Christiana" used Baybayin alongside Spanish and Chinese characters, demonstrating early attempts at cultural accommodation. However, this tactical inclusion served colonial objectives—using familiar scripts to transmit foreign religious concepts.
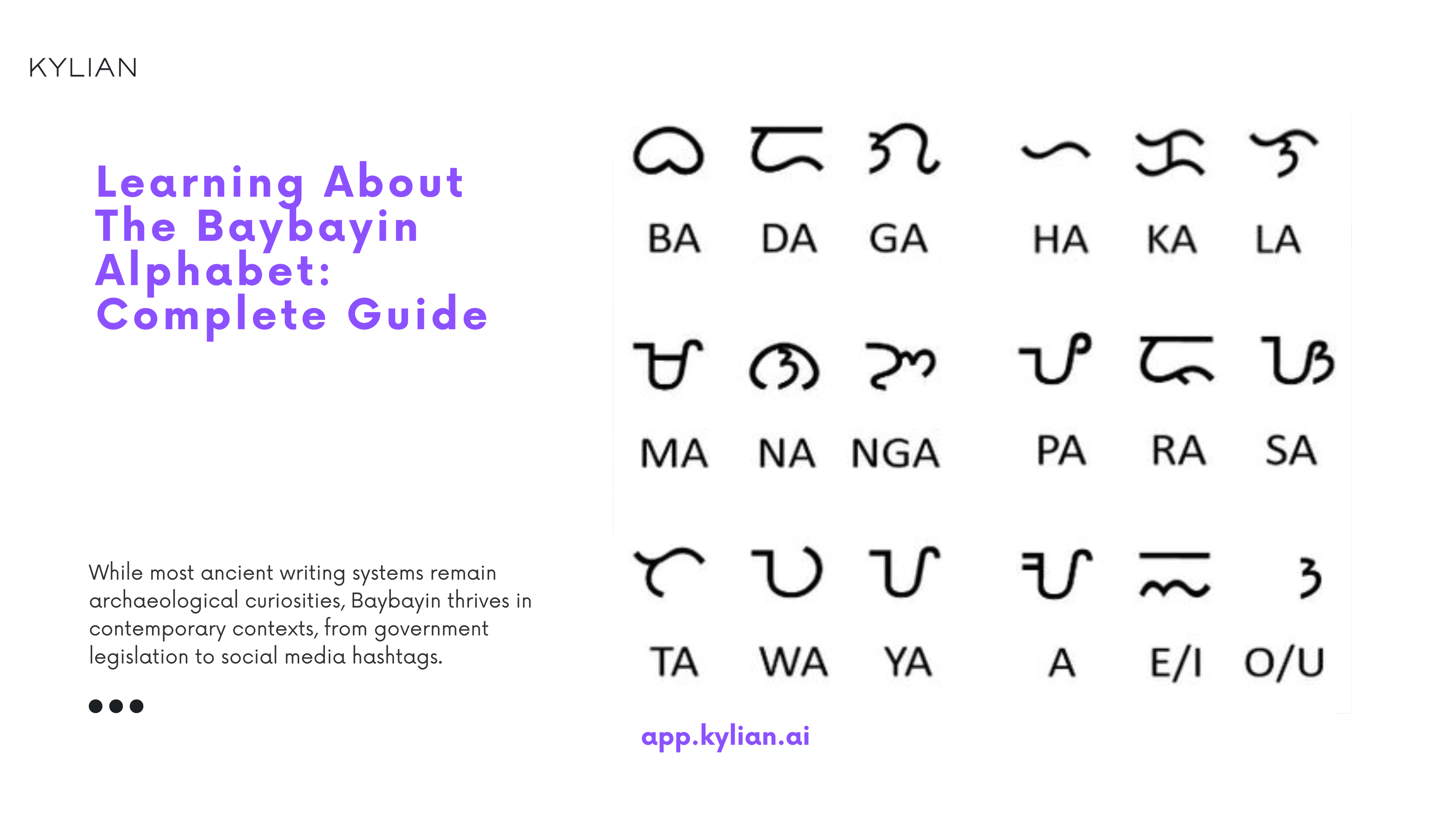
The Structural Logic of Baybayin as an Abugida
Baybayin's classification as an abugida rather than an alphabet reflects fundamental differences in how languages conceptualize sound-symbol relationships. While alphabetic systems assign individual symbols to discrete phonemes, abugidas organize around syllabic units. This distinction isn't merely technical—it reveals different approaches to linguistic analysis.
The system's 14 consonant characters and 3 vowel characters create a compact yet comprehensive framework for representing Tagalog phonology. Each consonant character inherently contains the vowel sound "a," establishing this as the default vocalization. This design principle reflects the phonological structure of Philippine languages, where open syllables predominate.
The vowel system's treatment of "e/i" and "o/u" as unified categories reflects historical phonological patterns in Tagalog. These weren't arbitrary choices but responses to actual sound systems. Modern Filipino retains traces of this pattern in words like "lalaki/lalake" (man), where vowel alternation doesn't change meaning—evidence of the script's linguistic accuracy.
The kudlit system demonstrates sophisticated phonetic analysis. Placing marks above characters for "e/i" sounds and below for "o/u" sounds creates visual logic that reinforces auditory patterns. This diacritical system predates similar European innovations by centuries, suggesting independent development of advanced orthographic principles.
The Spanish introduction of kudlit-krus (cross kudlit) to represent consonant clusters reveals the script's original limitations and colonial modifications. Traditional Baybayin couldn't represent final consonants without vowels, reflecting the syllabic nature of Philippine languages. The Spanish addition addressed this gap but also transformed the script's fundamental character.
Modern usage often overlooks this historical complexity. Contemporary Baybayin practitioners frequently mix traditional and Spanish-modified forms without acknowledging the distinction. This blending creates confusion about "authentic" Baybayin while obscuring the script's evolution under colonial influence.
Systematic Approach to Baybayin Writing Mastery
Learning Baybayin effectively requires understanding its phonetic foundation. The principle "write as you say it" distinguishes Baybayin from orthographically irregular systems like English. This phonetic consistency makes the script accessible once learners internalize its syllabic logic.
Character formation demands attention to the script's distinctive curves and proportions. Unlike angular alphabetic systems, Baybayin's flowing lines create aesthetic unity while maintaining functional clarity. Consistent practice with basic strokes builds muscle memory essential for fluent writing.
The vowel modification system requires systematic drill. Creating comprehensive charts showing all possible syllable combinations for each consonant builds familiarity with the kudlit system. This methodical approach prevents the random errors that plague casual learners.
Personal name transliteration provides meaningful early practice while highlighting the script's phonetic nature. Names like "Jennifer" become "Yeniper" in Baybayin because the script follows pronunciation rather than spelling. This exercise forces learners to think phonetically rather than orthographically.
Progressive vocabulary building moves from simple Filipino words to complex phrases. Beginning with culturally significant terms like "kapamilya" (family) or "pakikipagkapwa" (shared identity) connects script learning with cultural understanding. This approach makes practice sessions meaningful rather than mechanical.
Digital tools supplement traditional practice but require critical evaluation. Automated converters often make errors because they apply algorithmic rules without linguistic understanding. Baybayin.com and similar platforms serve as helpful references but shouldn't replace human guidance from knowledgeable practitioners.
Common Learning Obstacles and Strategic Solutions
The alphabetic mindset creates the most persistent learning barrier. Students consistently try to map Baybayin characters onto English letters, creating fundamental conceptual errors. Overcoming this requires explicit instruction about syllabic versus alphabetic organization principles.
Kudlit placement errors stem from inadequate practice with the diacritical system. Students often place marks randomly rather than following the "above for e/i, below for o/u" rule. Systematic drilling with syllable charts prevents these mechanical errors.
Foreign sound adaptation challenges learners attempting to write non-Filipino words. Baybayin lacks characters for sounds like "f," "v," "j," "z," and "x" because these sounds don't exist in traditional Philippine languages. Understanding this limitation requires phonological awareness about cross-linguistic sound systems.
Final consonant handling reveals the script's syllabic constraints. Traditional Baybayin couldn't represent word-final consonants without attached vowels. Students must choose between Spanish-modified forms (using kudlit-krus) or traditional approaches that leave final consonants implied.
Regional variation confusion arises from treating "Baybayin" as a monolithic system. What most people call Baybayin specifically refers to the Tagalog version. Related scripts like Kulitan (Kapampangan), Surat Mangyan (Mindoro), and Badlit (Visayan) have distinct characteristics. Understanding these differences prevents overgeneralization.
Character consistency problems emerge when students mix historical periods and regional styles. The script evolved over time and varied across geographic areas. Beginning learners benefit from choosing one consistent style rather than combining different versions arbitrarily.
Contemporary Baybayin Applications and Cultural Impact
The 2018 survey revealing that 57% of young Filipinos want to learn traditional Philippine scripts signals a significant cultural shift. This statistic represents more than academic interest—it reflects growing awareness that cultural identity includes intellectual traditions, not just food and festivals.
Government recognition through the proposed National Writing System Act demonstrates official acknowledgment of Baybayin's cultural importance. Requiring the script on street signs, public facilities, and food labels would make it functionally visible in daily life rather than confined to academic or artistic contexts.
Unicode integration represents crucial technical infrastructure for digital preservation. Including Baybayin in global character encoding standards ensures the script remains accessible across digital platforms. This technical inclusion prevents the digital divide from becoming another barrier to cultural transmission.
The tattoo culture phenomenon deserves critical analysis beyond surface aesthetics. Filipino tattoo traditions predate Spanish colonization, making contemporary Baybayin tattoos a revival rather than innovation. Spanish chroniclers documented extensive tattooing practices among early Filipinos, suggesting that inscribing cultural symbols on skin has deep historical precedent.
Corporate adoption by brands demonstrates Baybayin's commercial viability. Companies like Team Manila and Baybayin Clothing have built successful businesses around products featuring the script. This commercial success proves that cultural authenticity can coexist with economic sustainability.
Educational integration in Philippine schools represents systematic cultural reclamation. Organizations like Artikulo Uno and Baybayin Buhayin conducting workshops indicates grassroots commitment to cultural transmission. These initiatives matter because they create pathways for intergenerational knowledge transfer.
Technological Integration and Digital Preservation
Digital platforms have transformed Baybayin from historical artifact to living communication tool. Social media usage of Baybayin hashtags and posts demonstrates how ancient scripts can find contemporary relevance. This digital presence ensures the script reaches younger generations through familiar channels.
Mobile applications like the Baybayin keyboard for Android provide practical tools for daily usage. However, these applications require regular updates and community support to remain functional. The sustainability of digital tools depends on ongoing technical maintenance and user engagement.
Online learning resources have democratized access to Baybayin instruction. YouTube tutorials, interactive websites, and mobile apps make learning possible without geographic constraints. This accessibility matters particularly for Filipino diaspora communities seeking cultural connection.
Quality control remains challenging in digital environments. Automated translation tools and amateur tutorials often contain errors that propagate quickly online. The abundance of digital resources requires critical evaluation to separate accurate instruction from well-intentioned but incorrect information.
The Cognitive Benefits of Learning Ancient Scripts
Research in cognitive science suggests that learning different writing systems enhances neuroplasticity and cross-cultural understanding. Baybayin's syllabic structure exercises different cognitive pathways than alphabetic systems, potentially improving overall linguistic flexibility.
The phonetic awareness required for Baybayin mastery transfers to other language learning endeavors. Students who understand how sounds map onto syllabic units often demonstrate improved pronunciation and spelling abilities in other languages.
Cultural scripts provide windows into alternative ways of organizing human knowledge. Learning Baybayin reveals that alphabetic organization isn't universal or inevitable—other systems can be equally sophisticated and functional.
The meditative qualities of practicing curved script formation offer psychological benefits beyond linguistic learning. The flowing movements required for proper Baybayin writing can reduce stress while building cultural connection.
Future Prospects and Preservation Challenges
The sustainability of Baybayin revival depends on moving beyond symbolic usage toward functional integration. Using the script only for decorative purposes limits its development as a living communication system. Genuine revival requires expanding Baybayin into contemporary contexts like business communication, academic writing, and technical documentation.
Standardization presents both opportunities and risks. Establishing consistent character forms and usage conventions could facilitate learning and digital implementation. However, excessive standardization might eliminate regional variations that reflect the script's historical diversity.
Teacher training represents a critical bottleneck. Effective Baybayin instruction requires educators who understand both the script's technical aspects and cultural significance. Developing comprehensive teacher preparation programs could accelerate adoption in formal educational settings.
International recognition could enhance preservation efforts. Inclusion in global cultural heritage initiatives would provide resources and institutional support for documentation and transmission activities.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.

Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.

This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”

With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.

In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.

Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.

During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.

Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.

With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.

Similar Content You Might Want To Read

Biff Slang in English: Definition and Cultural Context
Language continuously evolves, reflecting societal shifts and cultural phenomena. Among the numerous colloquialisms that have entered modern English vocabulary, "biff" stands out as a particularly versatile slang term with multiple interpretations and applications across different English-speaking communities.

Beef in Slang: A Guide to Conflict in English
Conflict permeates human interaction across cultures, but the language we use to describe these tensions varies dramatically. In English-speaking communities, particularly within urban and youth cultures, "beef" has emerged as a powerful linguistic shorthand for disagreements, feuds, and conflicts. This terminology isn't merely casual vernacular—it represents a sophisticated social code that communicates the intensity, origin, and nature of interpersonal disputes. The concept of "beef" transcends simple disagreement. When someone references "having beef," they're signaling something more profound than a mere difference of opinion. They're pointing to a sustained conflict with emotional investment, often involving damaged pride, perceived disrespect, or violated boundaries. Understanding beef slang provides critical insight into social dynamics, especially in communities where direct confrontation may follow specific cultural protocols. The evolution of this terminology reflects broader social patterns. As communities develop mechanisms to navigate conflict, their language adapts accordingly. Beef slang doesn't just describe conflict—it provides a framework for categorizing it, addressing it, and sometimes, ritualistically resolving it.

Guide to Using 'Either...Or' and 'Neither...Nor' in English
Do you find yourself hesitating when using "either/or" and "neither/nor" in English? These seemingly simple word pairs are among the most frequently misused grammatical constructions, even by advanced English speakers. Mastering them is essential for clear, precise communication in both written and spoken English. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the proper use of these correlative conjunctions, with practical examples and clear explanations that will transform your understanding of these important grammatical structures.

60 English Verbs for Beginners: Building Your Foundation
Learning English requires a strategic approach. When faced with thousands of words to memorize, knowing which ones to prioritize makes all the difference in your progress. Verbs—the action words that drive your sentences—form the backbone of effective communication. Master the right ones first, and you'll achieve conversational ability much faster.

Punctuation Rules in English: Master Every Mark
Punctuation errors account for nearly 50% of score variability in professional writing assessments, making proper punctuation mastery not just a stylistic choice but a career-defining necessity. With roughly 50% of score variability explainable by error occurrences, the stated hypothesis is considered confirmed. Research consistently demonstrates that punctuation errors (n = 989) ranking first among grammatical mistakes in published academic writing, yet most professionals remain unaware of how these seemingly minor marks fundamentally alter meaning, credibility, and reader comprehension. The reality of modern communication demands precision. Every misplaced comma, incorrect apostrophe, or missing semicolon sends a signal about your attention to detail, professionalism, and communication competence. This comprehensive guide examines why punctuation rules matter now more than ever and provides the systematic framework needed to eliminate errors that undermine your written authority.

Better Ways to Say "I Like" and "I Don't Like" in English
Do you find yourself repeatedly using the same phrases to express your preferences? The ability to articulate what you enjoy or dislike with precision and variety not only enriches your conversations but also demonstrates language proficiency. This article explores alternative expressions to the common "I like" and "I don't like" statements, providing you with a diverse vocabulary arsenal to communicate your preferences more effectively.